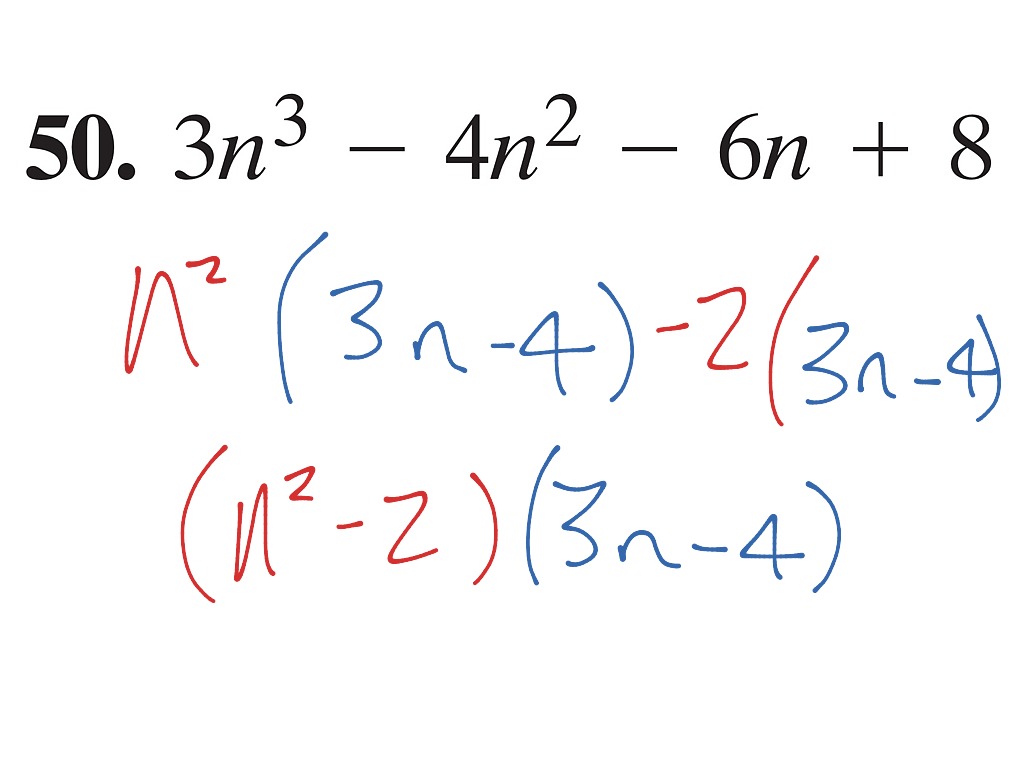
Factoring Examples Math, Algebra ShowMe
This is how the solution of the equation 2 x 2 − 12 x + 18 = 0 goes: 2 x 2 − 12 x + 18 = 0 x 2 − 6 x + 9 = 0 Divide by 2. ( x − 3) 2 = 0 Factor. ↓ x − 3 = 0 x = 3. All terms originally had a common factor of 2 , so we divided all sides by 2 —the zero side remained zero—which made the factorization easier.

Factoring Quadratic ax²+bx+c with ac
Factoring quadratics: leading coefficient = 1. Factoring quadratics as (x+a) (x+b) (example 2) More examples of factoring quadratics as (x+a) (x+b) Factoring quadratics with a common factor. Factoring completely with a common factor. Factoring simple quadratics review.

Factoring Quadratics The 'X' method. YouTube
Factors. Numbers have factors:. And expressions (like x 2 +4x+3) also have factors:. Factoring. Factoring (called "Factorising" in the UK) is the process of finding the factors:

Factoring YouTube
How to factor expressions. If you are factoring a quadratic like x^2+5x+4 you want to find two numbers that. Add up to 5. Multiply together to get 4. Since 1 and 4 add up to 5 and multiply together to get 4, we can factor it like: (x+1) (x+4)
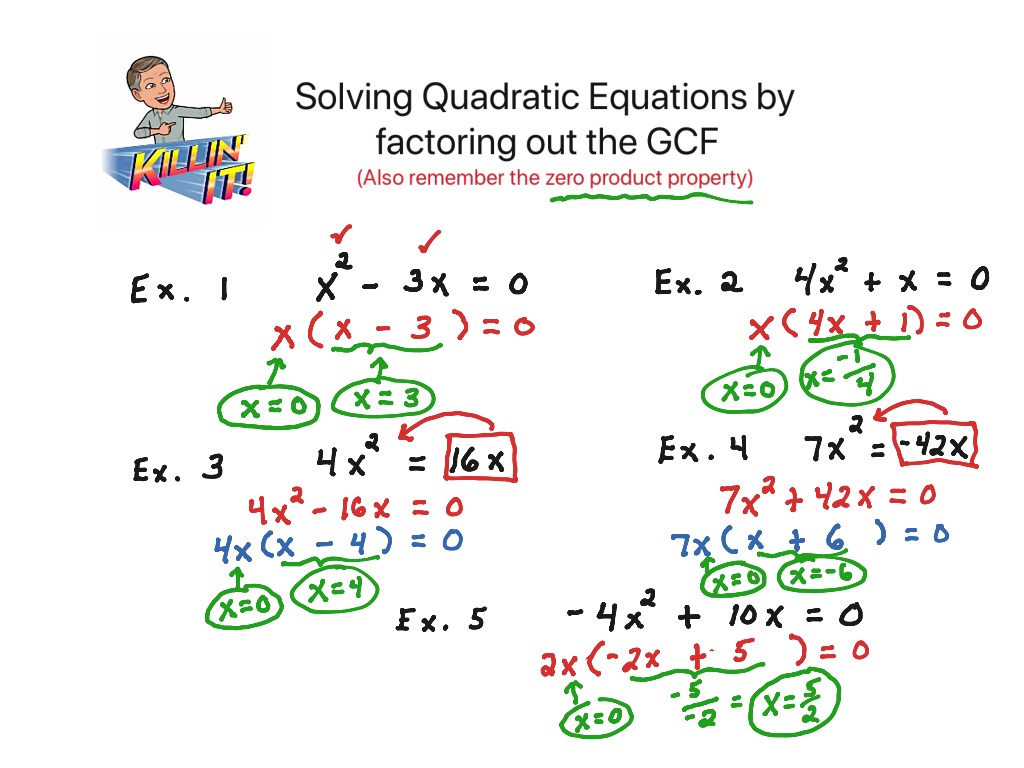
Factoring out GCF to solve quadratic equations Math, Algebra ShowMe
However, there is a common factor of 2 which we can factor out: 2x2 − 50 = 2(x2 − 25) The expression inside the parentheses is a difference of squares and should be factored: 2x2 − 50 = 2(x2 − 25) = 2(x + 5)(x − 5) Example 1.2.7. Factor 24 − 2x − x2.
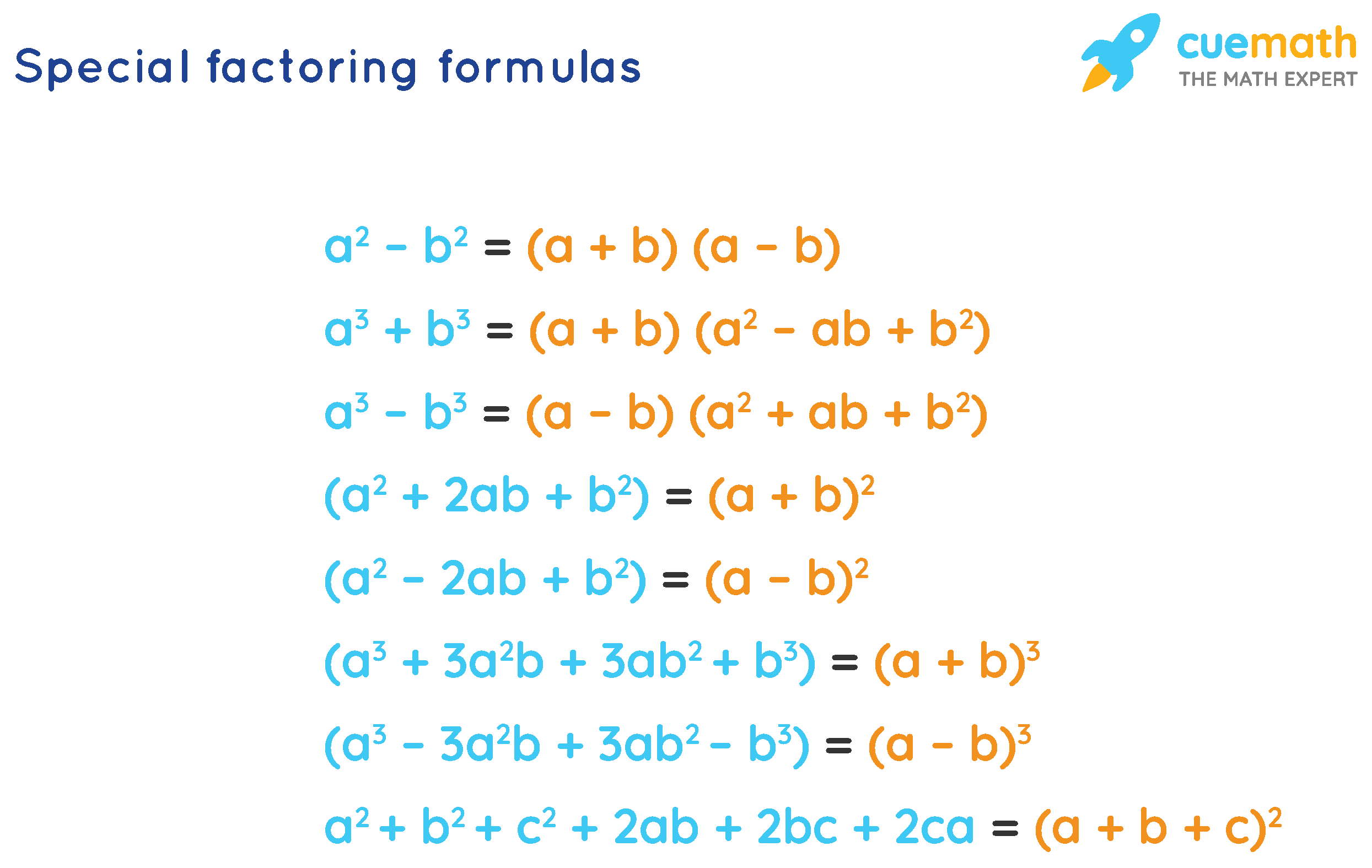
Factoring Formulas in Algebra What Are Factoring Formulas?
Illustrated definition of Factorising: Finding what to multiply to get an expression. Example: 2y6 2(y3), so the factors of 2y6 are: 2 and (y3).

3 formas de factorizar ecuaciones algebraicas wikiHow
In algebra, one method for solving equations is to factor them when possible. This is because factoring gives us an equation in the form of a product of expressions that we can set equal to 0. If the product of two (or more) expressions is equal to 0, as is the case when we factor polynomials, at least one of the expressions must equal 0.
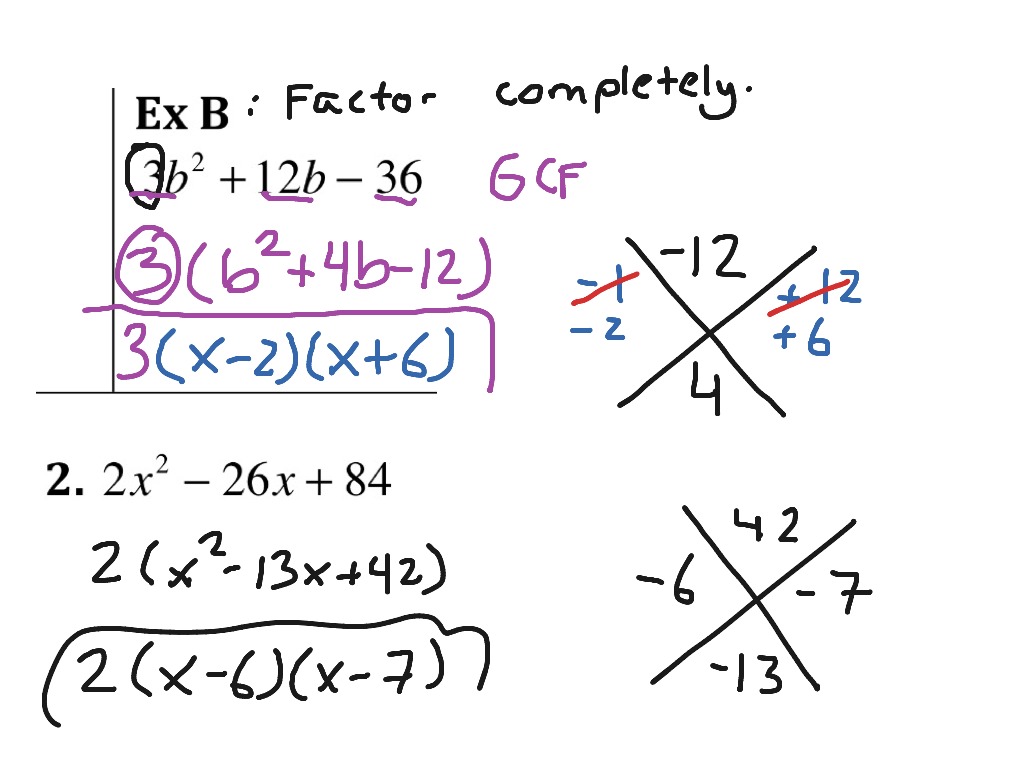
Algebra 85b Preview B, 2 Algebra, Quadratic Equations, Factoring ShowMe
To factor a binomial, write it as the sum or difference of two squares or as the difference of two cubes. How do you factor a trinomial? To factor a trinomial x^2+bx+c find two numbers u, v that multiply to give c and add to b. Rewrite the trinomial as the product of two binomials (x-u) (x-v)
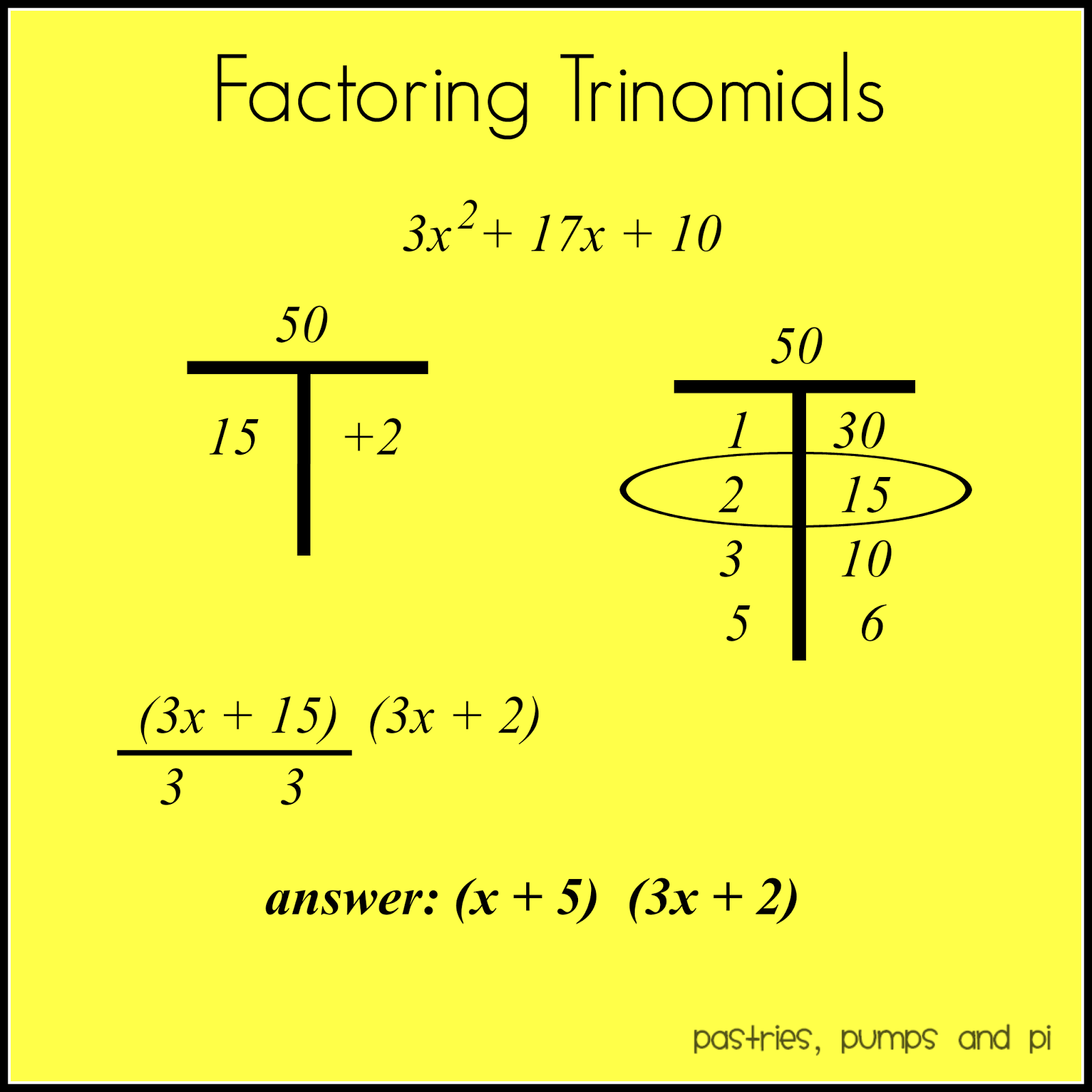
Math Tip Of The Day Factoring Trinomials Pastries, Pumps and Pi
👉Learn how to factor quadratics when the coefficient of the term with a squared variable is not 1. To factor an algebraic expression means to break it up in.
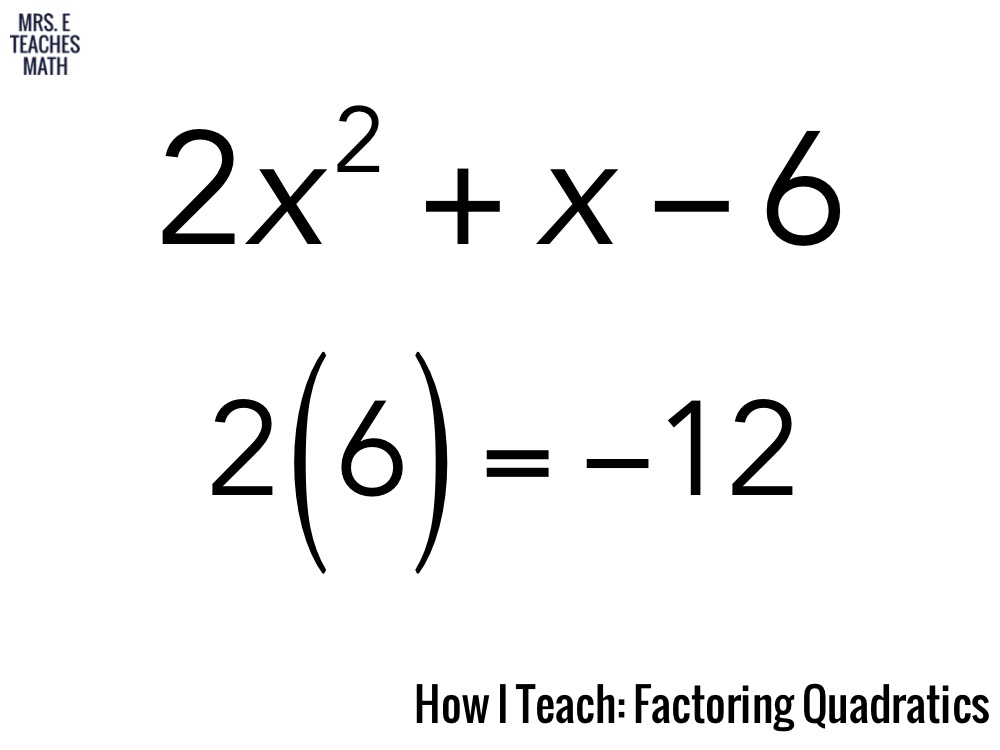
How I Teach Factoring Quadratics Mrs. E Teaches Math
Answer. y = 2 y = 2. [/hidden-answer] We could have used the distributive property and the addition and multiplication properties of equality to solve the equation in the previous example. It would look something like this: Solve 7(y − 2) = 0 7 ( y − 2) = 0 using the distributive property.
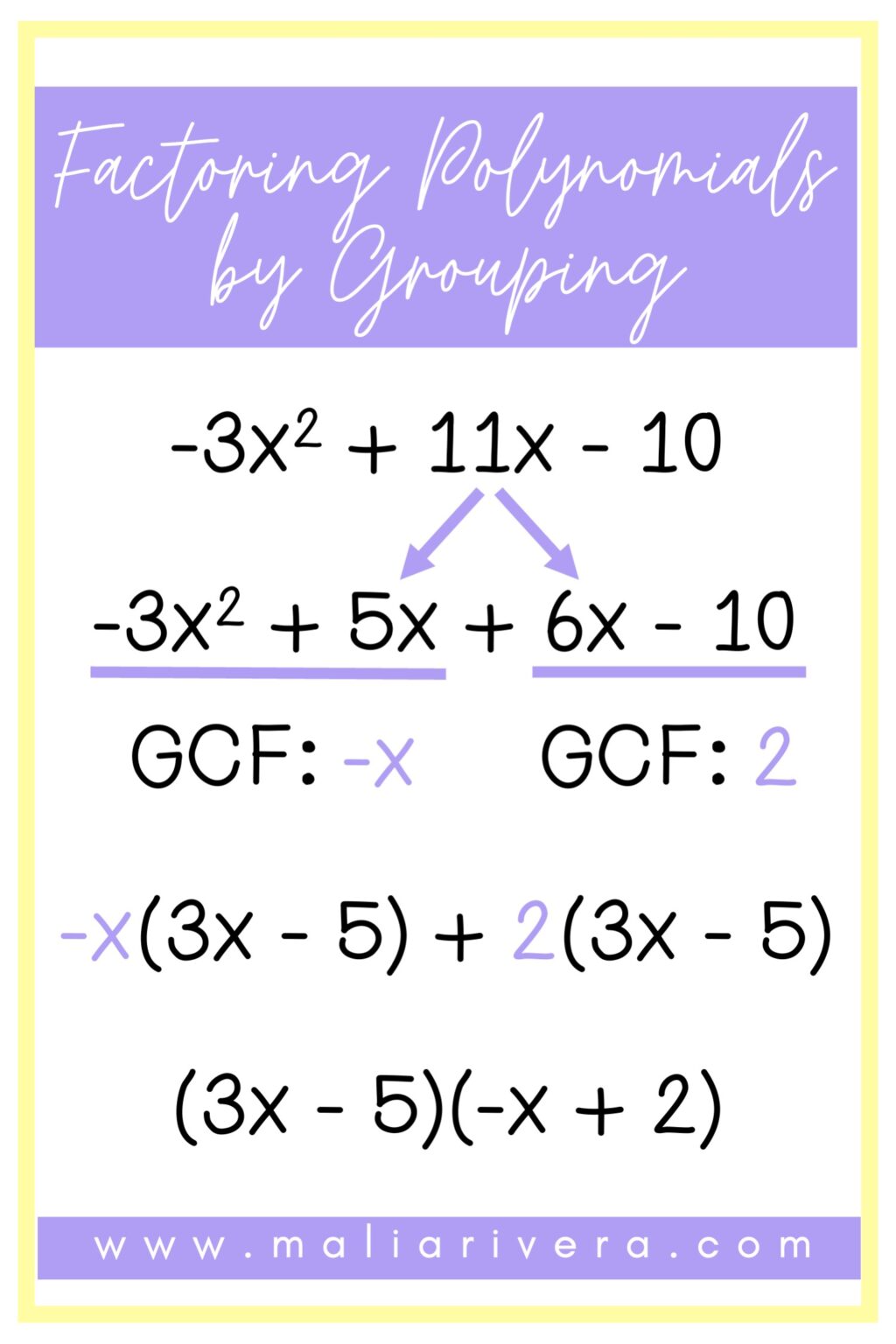
Teaching Students How to Factor Polynomials Maila Rivera
The polynomial x 2 + cx + d, where a + b = c and ab = d, can be factorized into (x + a)(x + b).. In mathematics, factorization (or factorisation, see English spelling differences) or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a product of several factors, usually smaller or simpler objects of the same kind.For example, 3 × 5 is an integer factorization of 15, and.

Gr 10 Applied Math Common Factoring
The numbers -15, -5, -3, -1, 1, 3, 5, and 15 are all factors of 15 because they divide 15 without a remainder. Factoring is an important process in algebra which is used to simplify expressions, simplify fractions, and solve equations. The next few lessons explain how to factor numbers, expressions, and equations. Factoring Numbers — Start Here.
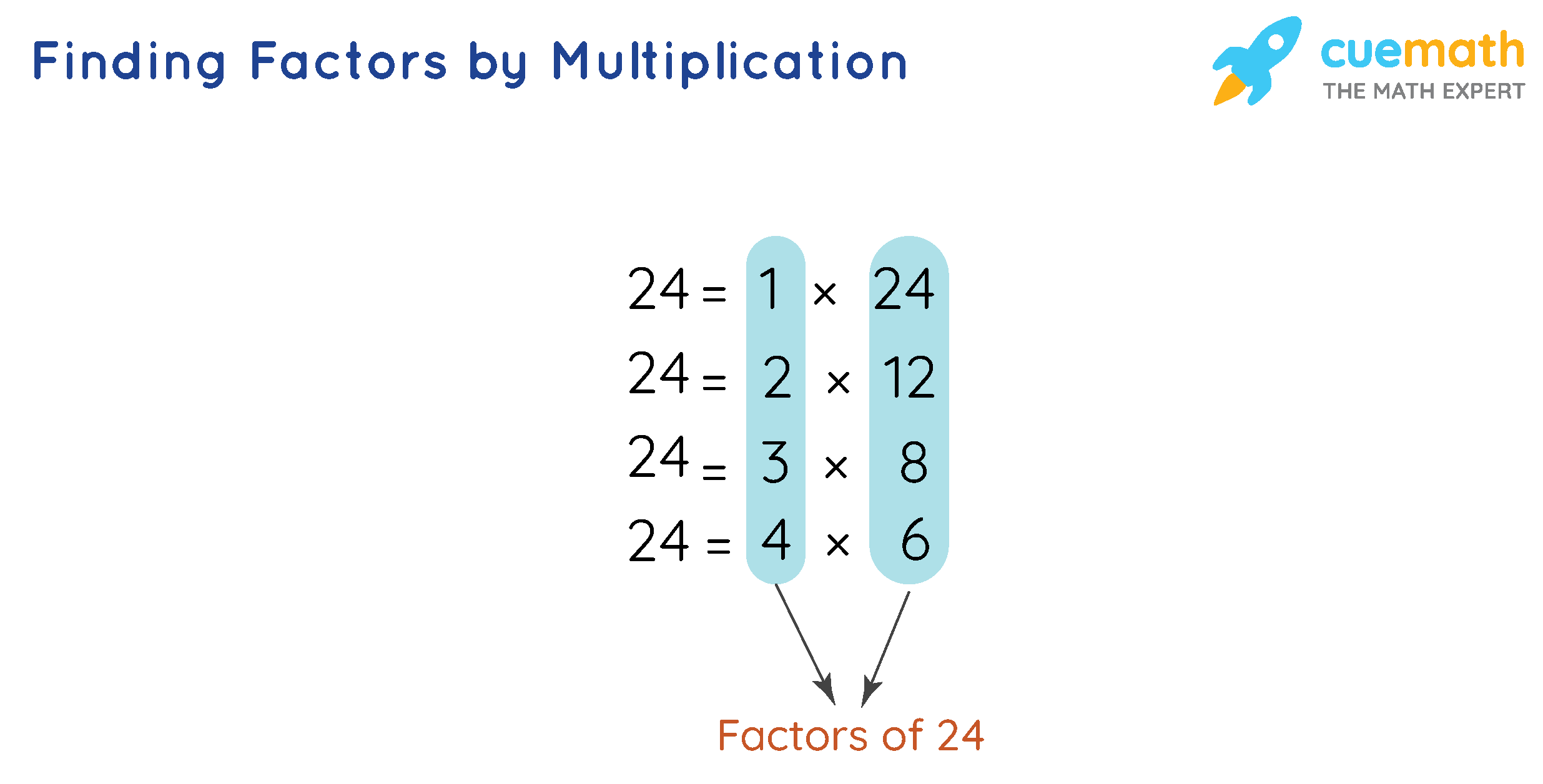
Factors How to Find Factors of a Number? Definition, Examples
Factorisation of an algebraic expression means writing the given expression as a product of its factors. These factors can be numbers, variables, or an algebraic expression. To the factor, a number means to break it up into numbers that can be multiplied to get the original number. For example, 24 = 4 × 6. 4 and 6 are the factors of 24. 9 = 3.
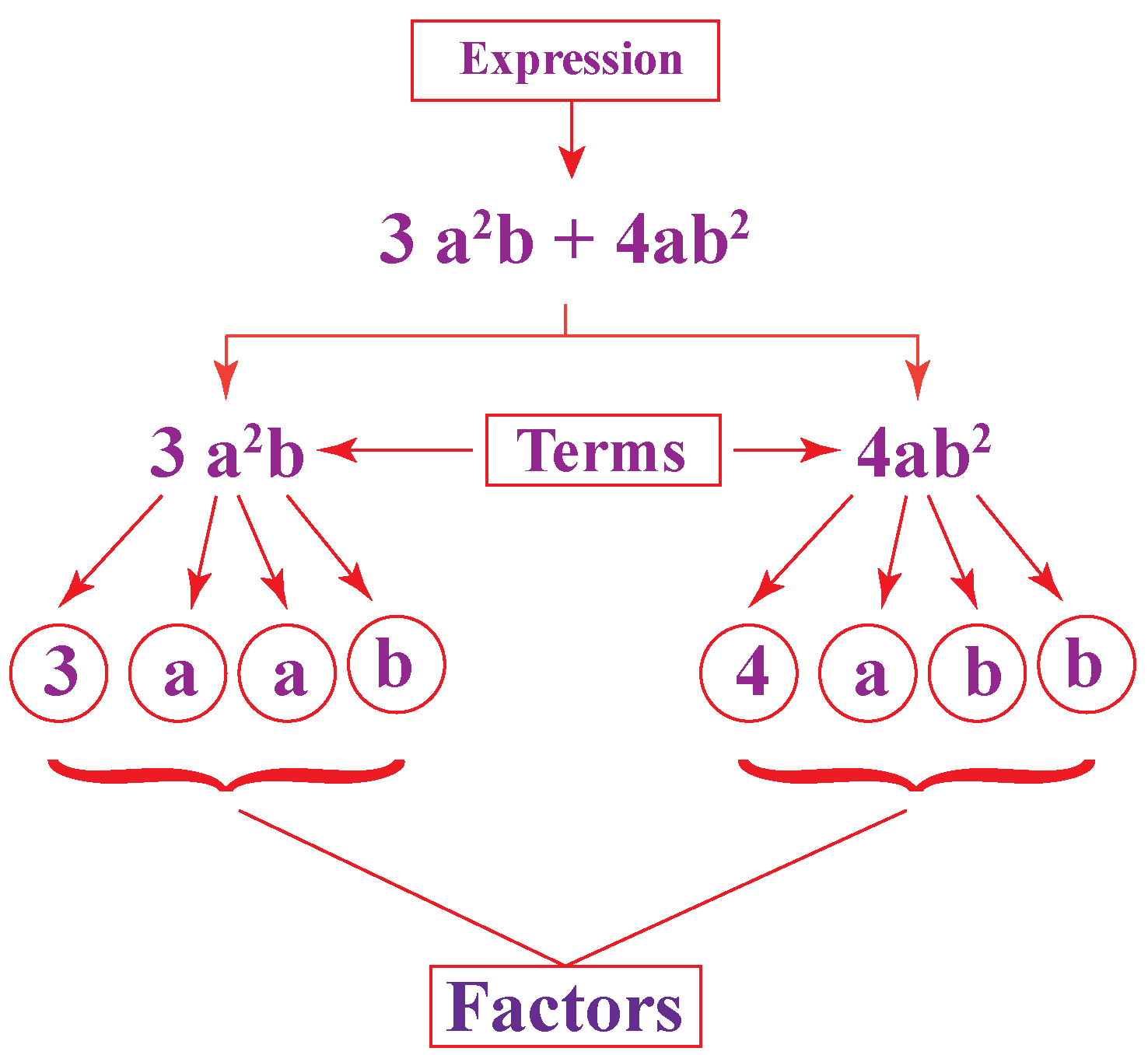
Factorization of Algebraic Expressions Identities Examples Cuemath
Because when I you have a quadratic in intercept form (x+a) (x+b) like so, and you factor it (basically meaning multiply it and undo it into slandered form) you get: x^2 + bx + ax + ab. This of course can be combined to: x^2 + (a+b)x + ab. So when you write out a problem like the one he had at. 5:39. x^2 + 15x + 50, 50, which is your "C" term.

Solving A Quadratic Equation By Factoring A Plus Topper
In this case, the GCF (6, 8) = 2. Step 2: Determine the common variable factors with smallest exponents. 6x5y3z and 8x2y3z2. In this case, the common variables with the smallest exponents are x2, y3, andz1. Step 3: The GCF of the monomials is the product of the common variable factors and the GCF of the coefficients.
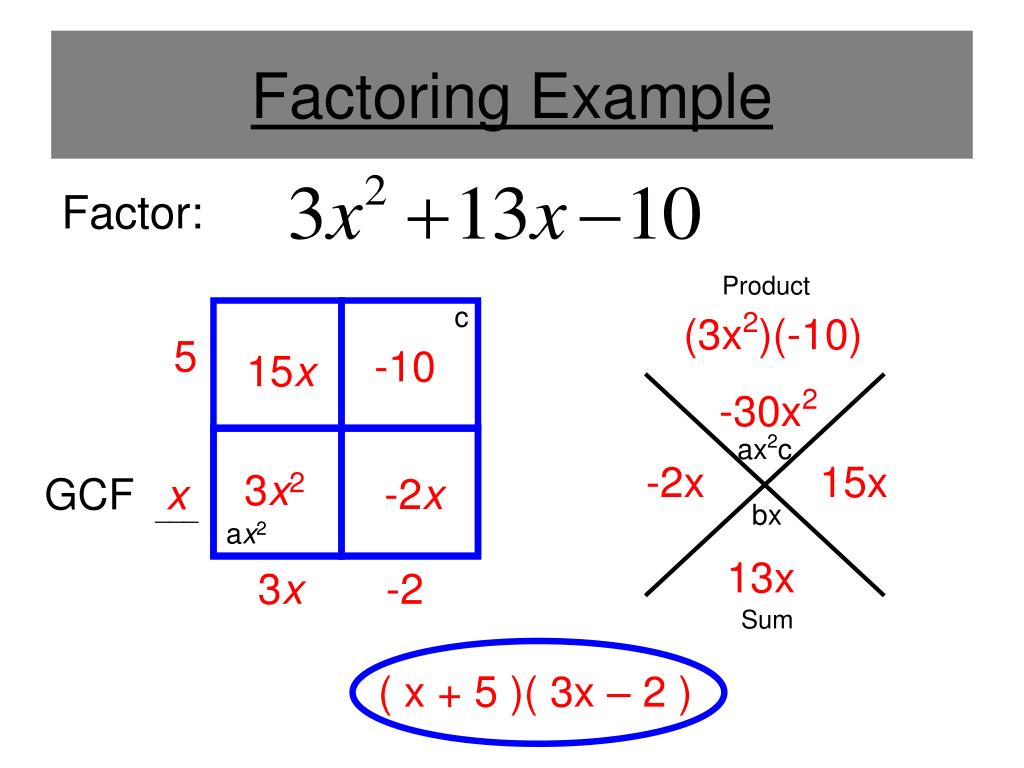
PPT Factoring Quadratic Expressions PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID2838817
Yes. The first term is a perfect square since 4 x 2 = ( 2 x) 2 , and the last term is a perfect square since 9 = ( 3) 2 . Also, the middle term is twice the product of the numbers that are squared since 12 x = 2 ( 2 x) ( 3) . We can use the perfect square trinomial pattern to factor the quadratic. = 4 x 2 + 12 x + 9 = ( 2 x) 2 + 2 ( 2 x) ( 3.